Hygromycin B
Description
Hygromycin B, an aminoglycoside antibiotic synthesized by Streptomyces hygroscopicus, inhibits protein synthesis by interfering with 70S ribosomal translocation and inducing misreading of mRNA template, thus killing prokaryotes (such as bacteria), eukaryotes (such as yeasts, fungi) and higher mammalian eukaryotes.
Hygromycin resistance genes (hyg or hph) derived from Escherichia coli encode hygromycin B phosphotransferase, which detoxifies hygromycin B into a non-biologically active phosphorylated product, making it an excellent selective marker for screening and culturing prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells successfully transfected with hytromycin resistance genes. In addition, due to different modes of action, Hygromycin B is often used in combination with G418 or Blasticidin S for the selection of dual-resistant cell lines. Hygromycin B can also be used as an antiviral agent because it selectively penetrates into cells with increased membrane permeability due to viral infection and inhibits translation. It can also act as an insect-repellant via mixed with animal feed.
Features
- High-quality raw materials, all antibiotic product raw materials are sourced from high-quality fixed suppliers
- Standardized production, using factory mass production mode
- Wide range of applications, which can be used in the fields of molecular biology and biochemical experimental research of tissue culture
- The cooperation platform covers the whole
- To ensure product quality stability, the difference between batches is controlled within 1%
Applications
- Screening of stably transfected cell lines
Specifications
|
Cat.No. |
60225ES03 / 60225ES10 |
|
Size |
1 g/10 g |
|
CAS No. |
31282-04-9 |
|
Molecular formula |
C20H37N3O13 |
|
Molecular weight |
527.52 g/mol |
|
Purity |
>90% (HPLC) |
|
Potency |
≥1050 U/mg |
|
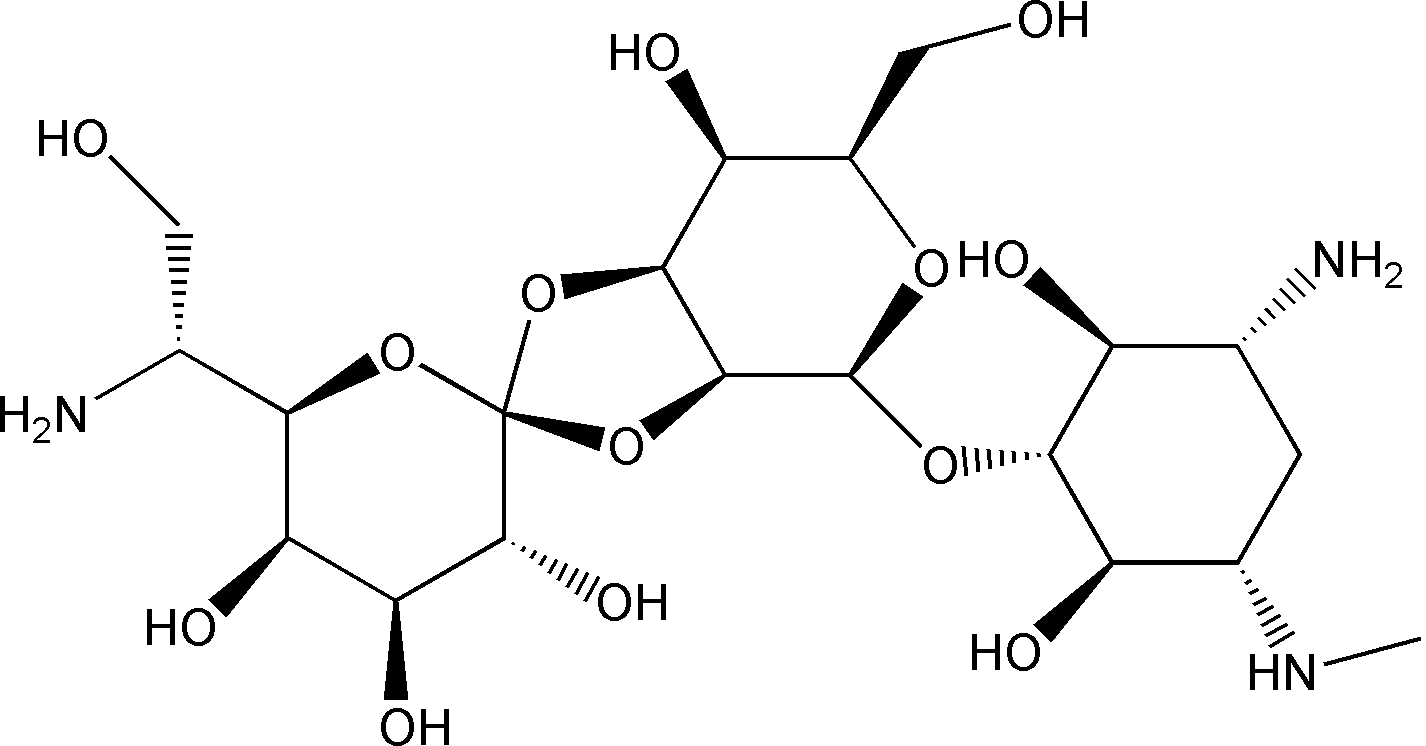
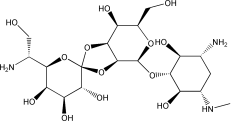
Structure |
|
Components
|
Name |
60225ES03 |
60225ES10 |
|
Size |
1 g |
10 g |
Storage
The product should be stored at -25~-15℃ for two years.
Figures
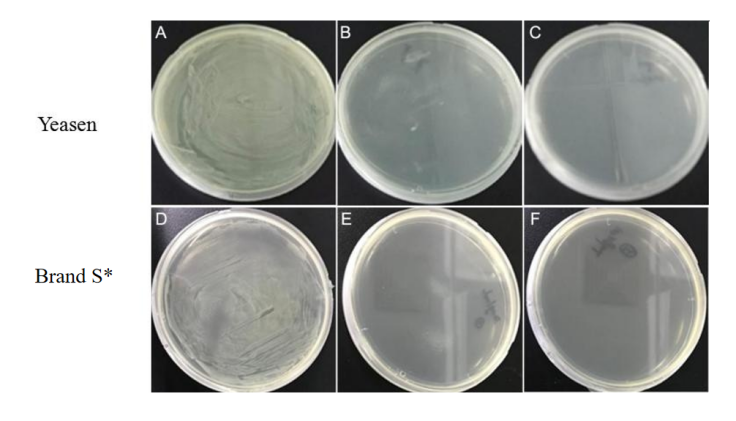
Figure 1 Colony growth of E. coli on hygromycin resistant plates with different concentrations, YEASEN and brand S* have the same effect
|
|
Figure 1 Colony growth of E. coli on hygromycin resistant plates with different concentrations, YEASEN and brand S* have the same effect
|
[1] Zhao Q, Zheng K, Ma C, et al. PTPS Facilitates Compartmentalized LTBP1 S-Nitrosylation and Promotes Tumor Growth under Hypoxia. Mol Cell. 2020;77(1):95-107.e5. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2019.09.018(IF:14.548)
[2] Zhu GD, Yu J, Sun ZY, et al. Genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screening identifies CARHSP1 responsible for radiation resistance in glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(8):724. Published 2021 Jul 21. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04000-3(IF:8.469)
[3] Chen J, Huang Y, Tang Z, et al. Genome-Scale CRISPR-Cas9 Transcriptional Activation Screening in Metformin Resistance Related Gene of Prostate Cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;8:616332. Published 2021 Jan 26. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.616332(IF:6.684)
[4] Jiang Z, Cui Z, Zhu Z, et al. Engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica transporters for high-efficient production of biobased succinic acid from glucose. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021;14(1):145. Published 2021 Jun 27. doi:10.1186/s13068-021-01996-w(IF:6.040)
[5] Liu Y, Jiang X, Cui Z, Wang Z, Qi Q, Hou J. Engineering the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for production of α-farnesene. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019;12:296. Published 2019 Dec 23. doi:10.1186/s13068-019-1636-z(IF:5.452)
[6] Cui Z, Zheng H, Jiang Z, et al. Identification and Characterization of the Mitochondrial Replication Origin for Stable and Episomal Expression in Yarrowia lipolytica. ACS Synth Biol. 2021;10(4):826-835. doi:10.1021/acssynbio.0c00619(IF:5.110)
Catalog No.:*
Name*
phone Number:*
Lot:*
Email*
Country:*
Company/Institute:*