Aureobasidin A (AbA)
Description
Aureobasidin A, also known as AbA, Basifungin, breomycin A, is a cyclic ester peptide antibiotic isolated from the filamentous fungus Aureobasidium Pullulans No. R106. It has a strong anti-fungal ability and is an inhibitor of the inositol phosphorylated ceramide synthase AUR1. It is toxic to yeast even at lower concentrations (0.1-0.5 μg/mL). Species of fungus susceptible to Aureobasidin A include Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharces pombe, Candida glabrata, Aspergillus nidulans, and A. niger.
AbA inhibits the activity of inositol phosphorylamide (IPC) synthase, an essential enzyme for fungalsphingolipid biosynthesis, and interferes with sphingolipid synthesis, thus killing the strain. AUR1 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and AURA gene from Aspergillus aspergillus, homologous genes encoding IPC synthase, are the most studied. Mutations in these genes can make strains resistant to AbA, such as AUR1-C gene.
Features
- High-quality raw materials, all antibiotic product raw materials are sourced from high-quality fixed suppliers
- Standardized production, using factory mass production mode
- Wide range of applications, which can be used in the fields of molecular biology and biochemical experimental research of tissue culture
- The cooperation platform covers the whole
- To ensure product quality stability, the difference between batches is controlled within 1%
Applications
- Yeast two-hybrid studies
- Yeast one-hybrid studies
- Drug-selectable marker in yeast
Specifications
| Synonym | Aureobasidin A; AbA; Basifungin |
| CAS No. | 127785-64-2 |
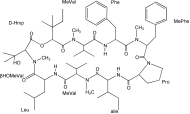
| Molecular formula | C60H92N8O11 |
| Molecular weight | 1101.42 g/mol |
| Appearance | liquid solution |
| Purity | ≥97% |
| Solubility | The powder is soluble in DMSO and methanol (0.5-10 mg/mL); Insoluble in water |
| Structure |
|
Components
| Components No. | Name | 60231ES03 | 60231ES08 | 60231ES10 |
| 60231 | Aureobasidin A (AbA) | 1 mg | 5×1 mg | 10×1 mg |
Shipping and Storage
The product is shipped with dry ice and can be stored at -15℃ ~ -25℃ for two years. Long-term storage at 4℃ and room temperature is not recommended. Aqueous stock solutions and store at -15℃ ~ -25℃. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw.
Figure
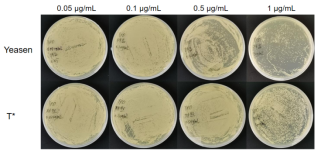
Figure 1 Yeast plate growth chart
Experimental strain: GS115
Usage amount: 0.05 μg/mL, 0.1 μg/mL, 0.5 μg/mL, 1 μg/mL
Treatment: 3-5 Days at 30℃
The upper row is the yeasen product, and the lower row is the brand T *.
[1] Zhang S, Zhang Y, Li K, et al. Nitrogen Mediates Flowering Time and Nitrogen Use Efficiency via Floral Regulators in Rice. Curr Biol. 2021;31(4):671-683.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2020.10.095(IF:10.834)
[2] Wang Y, Li D, Gao J, et al. The 2'-O-methyladenosine nucleoside modification gene OsTRM13 positively regulates salt stress tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot. 2017;68(7):1479-1491. doi:10.1093/jxb/erx061(IF:5.830)
[3] Dong H, Tan J, Li M, et al. Transcriptome analysis of soybean WRKY TFs in response to Peronospora manshurica infection. Genomics. 2019;111(6):1412-1422. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2018.09.014(IF:2.910)
Catalog No.:*
Name*
phone Number:*
Lot:*
Email*
Country:*
Company/Institute:*