Introduction
Neural stem cells (NSCs) exist in the nervous system, which can differentiate into neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, and can self-renew, thereby producing a large number of brain cells.
B-27 and N-2 are widely used in neural stem cell culture, B-27 is an optimized serum-free supplement to support the growth and maintenance of neuronal activity in hippocampal neurons and other central nervous system (CNS).
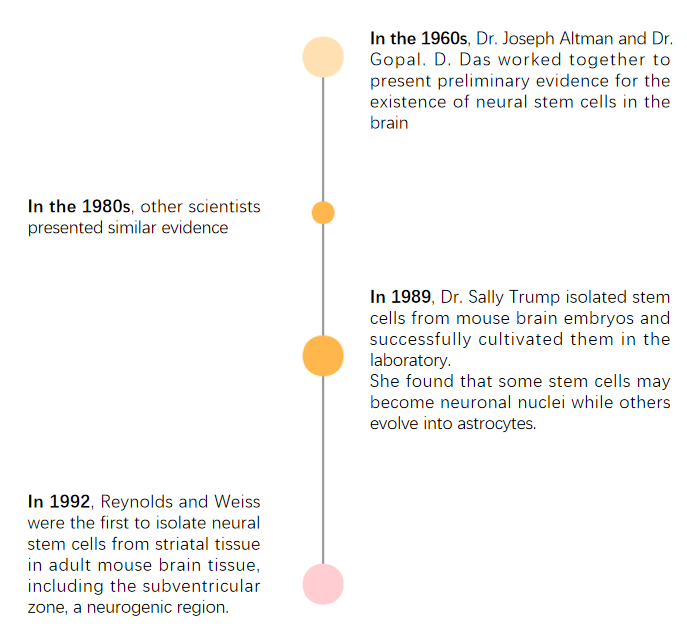
Figure 1. The development process of neural stem cells
Nervous System Diseases and Treatment Mechanisms
Nervous system diseases refer to diseases that occur in the central nervous system or peripheral nervous system and are mainly manifested by disturbances such as sensation, consciousness, and movement. Including Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), multiple sclerosis, Huntington's disease, cerebellar atrophy, spinal cord injury, traumatic brain injury and other diseases.
The therapeutic mechanism of neural stem cells: (A) After tissue damage in the diseased site, various chemokines are released, which can attract neural stem cells to aggregate to the damaged site and differentiate into different types of cells, thereby repairing damaged nerve cells. (B) Neural stem cells can secrete a variety of neurotrophic factors and promote the repair of damaged cells.(C) Neural stem cells can strengthen connections between synapses and build new neural circuits.
Application of N-2
1. Differentiating glial precursor cells into astrocytes
Astrocytes are multifunctional glial cells of the central nervous system. They participate in the physical structure of the brain and play important roles in supporting nerve cells, maintaining ion concentration around neurons, and immune regulation. Glial precursor cells (GPCs), also known as glial restricted progenitors (GRP) or oligodendrocyte progenitor cells(OPCs), are cells that have the potential to differentiate into oligodendrocytes or astrocytes. The GPC population is derived from tissue or is generated from pluripotent cells by differentiation, which is induced by exogenously applied factors. Here we describe a culture system that can be adjusted to favor differentiation into either astrocytes or oligodendrocytes.
Experimental procedure
1) Astrocyte differentiation medium
|
Components |
Amount (mL) |
|
DMEM, 1X |
97 |
|
N-2 Supplement,Serum Free,100X |
1 |
|
FBS |
2 |
2) Experimental process
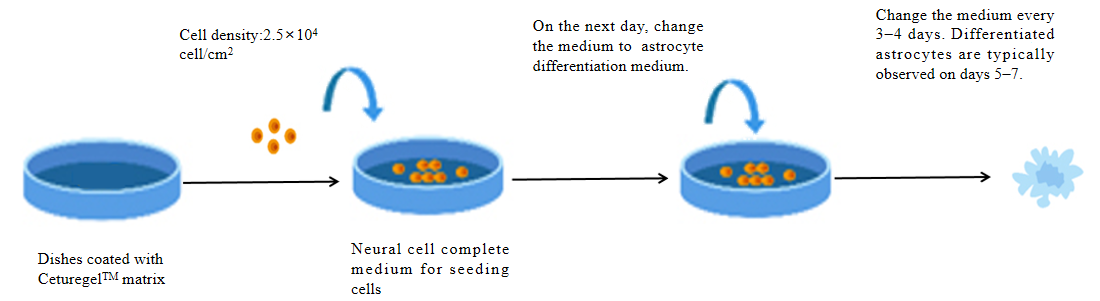
Figure 2. Flow chart of the experiment for the differentiation of glial precursor cells into astrocytes
2. Culture of cytoplasmic astrocytes
Astrocytes are the most abundant glial cell type in the central nervous system (CNS) and are responsible for a range of functions required to support the activity of cortical circuits.They are involved in adult CNS homeostasis, biochemical and nutritional support of neurons and endothelial cells that form the blood-brain barrier, perform the vast majority of synaptic glutamate uptake, and maintain extracellular potassium levels.
Experimental procedure
1) Preparation of culture medium
|
Components |
Amount (mL) |
|
DMEM, 1X |
88 |
|
N-2 Supplement,Serum Free,100X |
1 |
|
FBS |
10 |
|
penicillin-streptomycin |
1 |
|
Optional addition: EGF ( prepared to 100 μg/mL stock solution) |
0.02 |
【Note】 Epidermal growth factor (EGF) can also be added to enhance astrocyte proliferation.
2) Experimental process
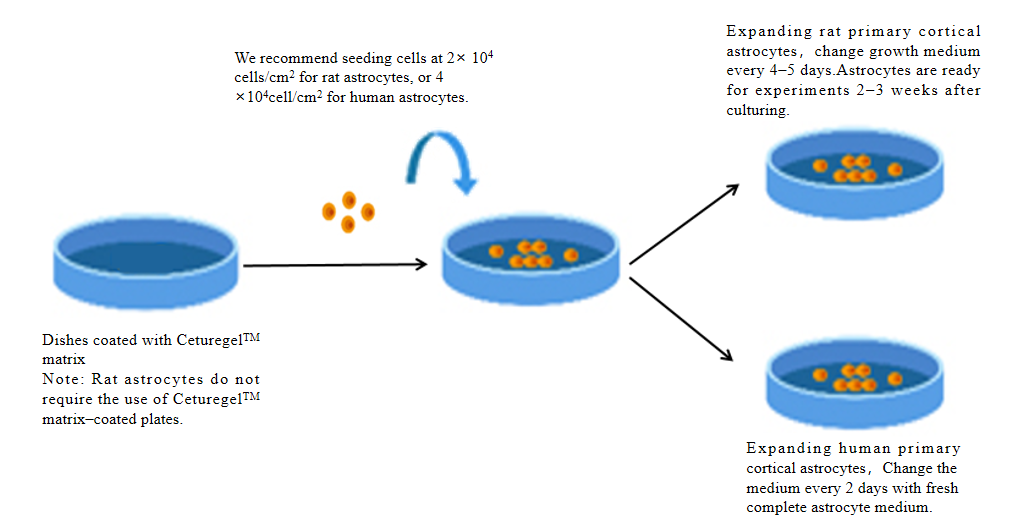
Figure 3. The flow chart of the culture experiment of stromal astrocytes
Tips for nouns:
Nerves are made up of bundles of nerve fibers. The nerve fiber itself is composed of multiple neuron cells, and the neuron structure is outside the axon and is covered by the myelin sheath formed by glial cells. Such nerves can transmit information from one part of the animal's body to another, so that the animal can coordinate and direct actions and perform various tasks.
Neuron , also known as neuron or nerve cell, is one of the structural and functional units of the nervous system. There are about 86 billion nerve cells in the human brain.
Neural stem cells (NSCs) , are self-renewing pluripotent cells that differentiate into the major phenotypes of the nervous system. These cell types include neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes.
Neural progenitor cells (NPCs) , are the progeny of stem cell divisions that typically undergo a limited number of replication cycles in vivo. There are many "specialized" cells in the brain, such as nerve cells, oligodendrocytes and astrocytes. Nerve cells transmit and receive information. Oligodendrocytes wrap around nerve cells and help them transmit information more quickly. Astrocytes (star cells) support the nervous system by providing nutrients and regulating access to the brain from other parts of the body.
Product advantages:
👍1、Efficient cultivation, good quality;
👍2、Strict quality control, strict sterility, no endotoxin;
👍3、The batch is stable and the difference between batches is small;
👍4、Fast delivery time, available from stock.
Ordering reagents:
|
Product Name |
Cat# |
Specifications |
|
|
B-27 supplement, serum free, 50X (Inquire) |
60703ES |
10mL |
|
|
B-27 supplement without Vitamin A, serum free, 50X (Inquire) |
60704ES |
10mL |
|
|
B-27 supplement, minus antioxidants, serum free, 50X (Inquire) |
60705ES |
10mL |
|
|
N-2 supplement, serum free, 100X (Inquire) |
60706ES |
5 mL |
|
|
Penicillin-Streptomycin (100×), Suitable for Cell culture (Inquire) |
60162ES |
100mL |
|